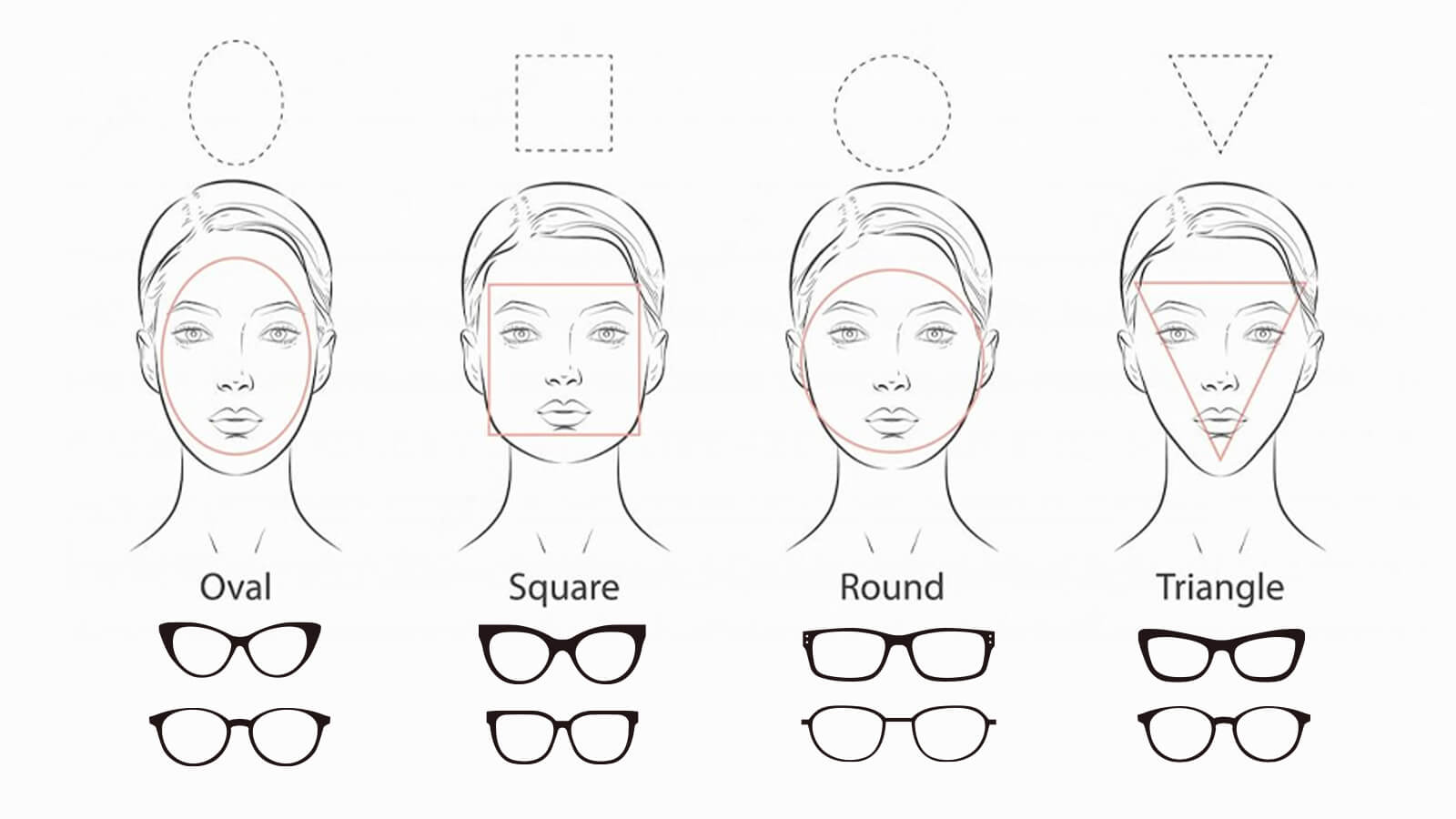
Guide to Picking Glasses That Suit Your Face Shape Perfectly
February 27,2023

What is Boho Style? A Comprehensive Guide to Boho-Chic Fashion
February 13,2025

Virtual Glasses Try On - Find Your Perfect Pair Online
April 02,2024

UV Protection Glasses VS. Blue Light Glasses - Vooglam
July 20,2023

The Ultimate Guide to Modern Trendy Men's Glasses: Top Styles for 2026
March 01,2024

Stylish Reading Glasses: Blending Fashion with Functionality
February 16,2023

Photochromic Lenses 101: How They Work & Why You Need Them
September 22,2023

Brown Eyes: The Beauty of the Most Common Hue
September 01,2024

The chubby face glasses for round face female
August 02,2023

What are prisms in eyeglasses?
March 20,2023

What Are Bifocal Glasses? The Complete Guide (Types, History & Benefits)
April 14,2023

How to Read Your Eyeglass Prescription?
March 11,2023
How to Tell If Your Sunglasses Are Polarized (3 Simple At-Home Tests)
Ever looked at your favorite pair of sunglasses and wondered if they’re actually polarized? It’s a common question, and it's frustrating not to be sure if you're getting the glare-blocking power you need. After all, your eyewear is a key part of your self-expression, but it also has an important job to do.
The intense, blinding light that reflects off a wet road or a lake isn't just brightness; it's a form of "visual noise" called glare. This glare can obscure details, wash out colors, and cause serious eye strain. While standard sunglasses can dim the scene, only polarized lenses are specifically engineered to eliminate this disruptive noise.
The good news is that you don't need to be an optics expert to find out if your lenses are up to the task. We will walk you through three simple methods to check for polarization and dive into the science of how it all works.
- 3 Proven Ways to Test for Polarization at Home
- What Are Polarized Lenses, Anyway? The Science of Seeing Clearly
- Polarized vs. Non-Polarized Lenses: What's the Real Difference?
- Are Polarized Sunglasses Actually Better for You?
- When Polarization Might Not Be the Best Choice
- A Crucial Clarification: Polarization vs. UV Protection
- Conclusion: Make a Confident Choice
3 Proven Ways to Test for Polarization at Home
You don't need any special equipment to verify your lenses—in fact, you probably have everything you need within arm's reach right now.
Method 1: The Screen Test (The Most Reliable Method)

This is the quickest and most definitive way to check for polarization. It works because the Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) on most modern screens emit polarized light to function.
- Grab your sunglasses and a digital screen, like your smartphone, tablet, or laptop.
- Turn the screen on to a bright, preferably white, background.
- Hold your sunglasses about 6-8 inches in front of the screen and look through one of the lenses.
- Slowly rotate your sunglasses 90 degrees (from a horizontal to a vertical position).
If the lenses are polarized, you’ll notice the screen becoming significantly darker or completely black. This happens because the two polarizing filters—the one in your screen and the one in your glasses—are now oriented at opposing angles, canceling each other out. If there's no change, the lenses are not polarized.
Method 2: The Glare Test (See the Difference in Real-Time)
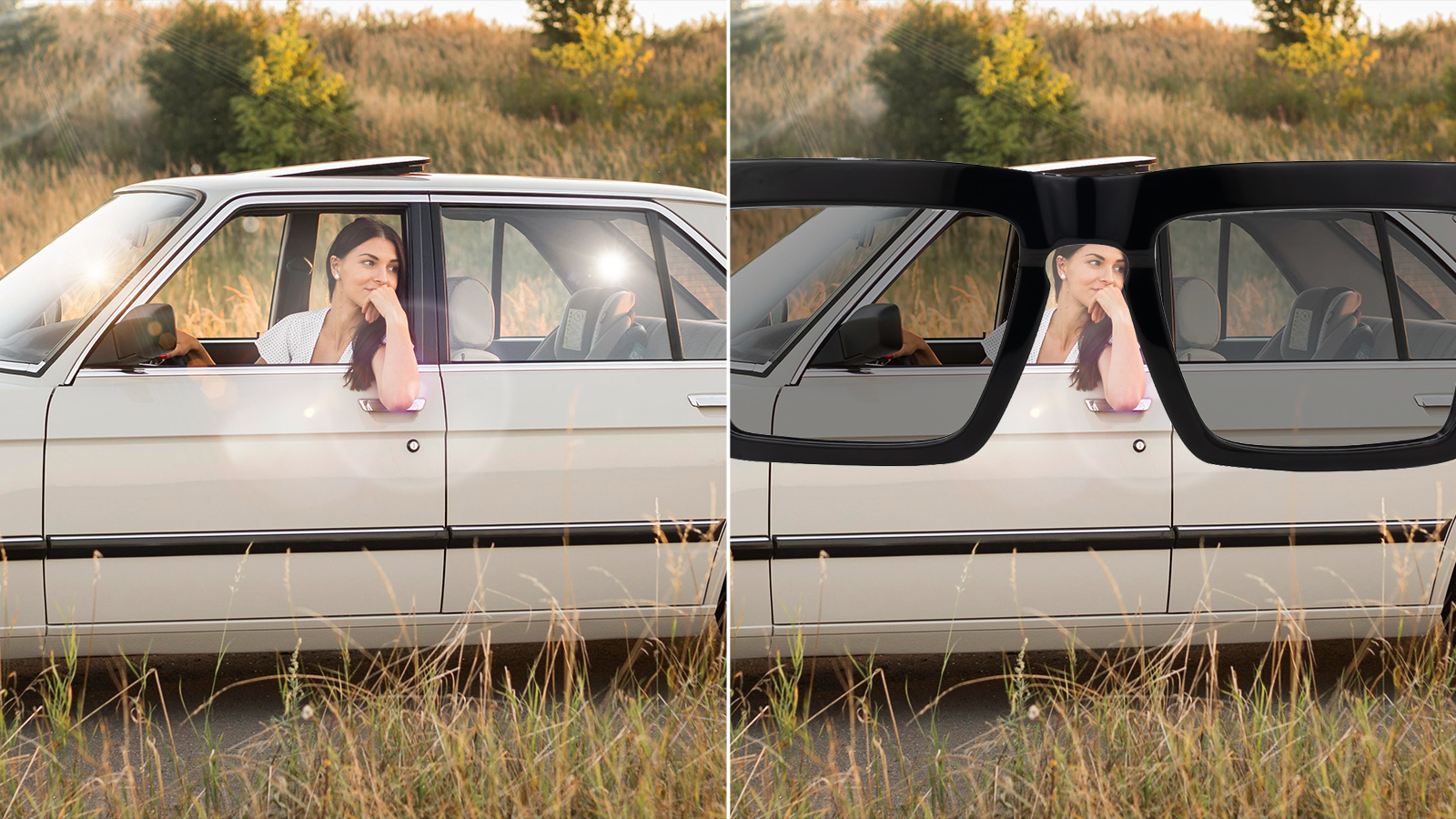

This test directly observes the primary function of the lenses: their ability to reduce reflected glare.
- Find a flat, reflective surface that’s producing a lot of glare. A car windshield, a puddle on a sunny day, or even a shiny tabletop will work perfectly.
- Stand a few feet back and look at the intense glare.
- Put on your sunglasses and look at the same spot.
If your sunglasses are polarized, the glare will be dramatically reduced or eliminated. You'll be able to see the surface with much greater clarity because the lenses are successfully filtering out the visual noise.
Method 3: The Two-Pair Test (Comparing Lenses)
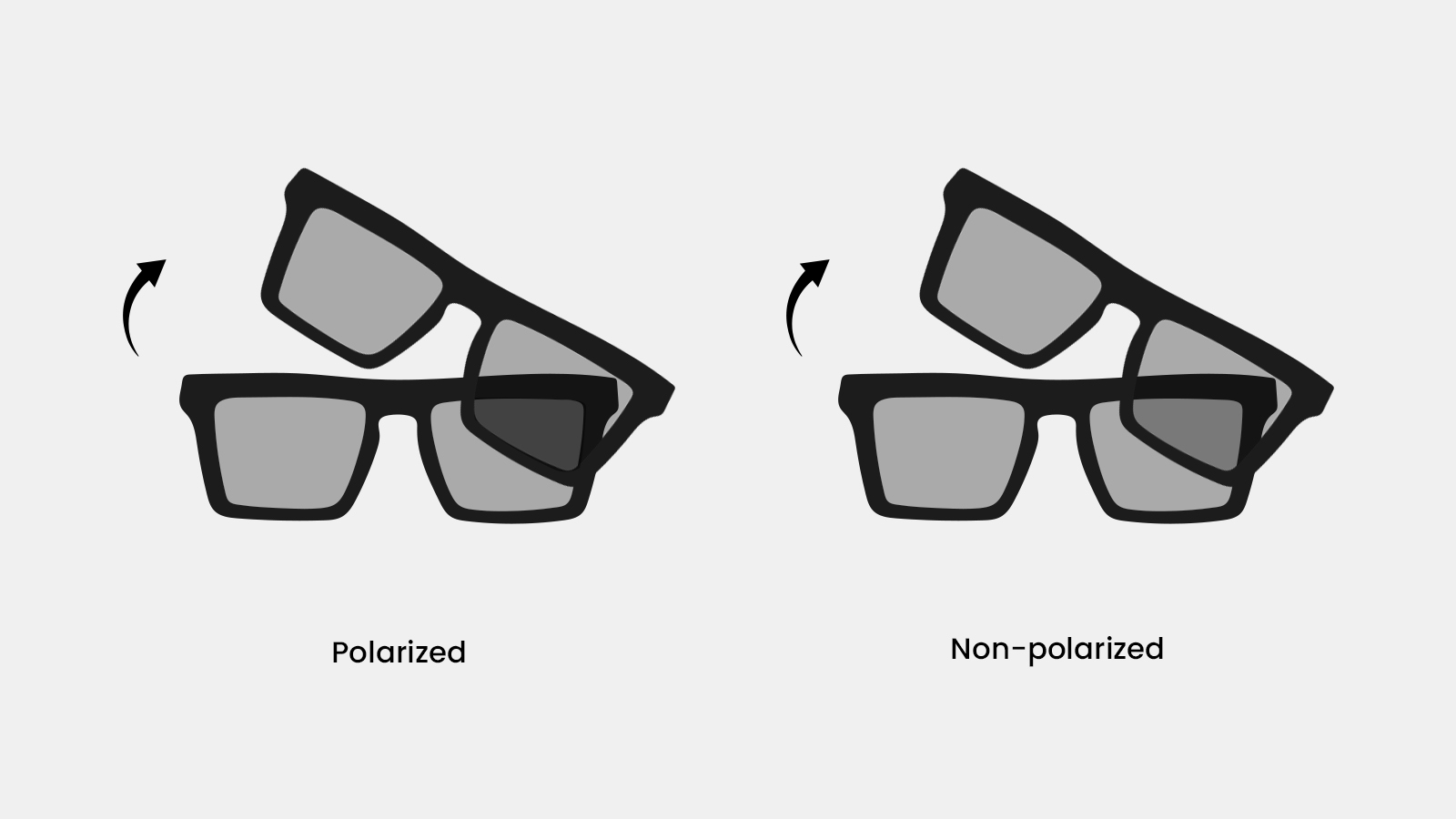
If you have another pair of sunglasses that are polarized, you can use them as a baseline.
- Hold up the known polarized pair and look through it.
- Take your second pair and hold them in front of the first pair, so you’re looking through both sets of lenses.
- Rotate the second pair 90 degrees.
If both pairs are polarized, the overlapping area of the lenses will turn completely dark, blocking all light from passing through.
What Are Polarized Lenses, Anyway? The Science of Seeing Clearly
It can feel like magic, but the science is straightforward and fascinating. Light from the sun travels in waves that vibrate in all directions—this is known as unpolarized light.
When these light waves strike a flat surface like a road or a body of water, they reflect and become organized. Instead of vibrating randomly, they concentrate in a single, side-to-side direction. This horizontally polarized light is what your eyes perceive as intense, blinding glare.
A polarized lens is an elegant solution to this problem. During manufacturing, a thin polyvinyl acetate (PVA) film is heated, stretched, and treated with iodine. This process forces the long-chain molecules within the film to align perfectly in a vertical pattern. This film is the polarizing filter.
Think of this filter as a microscopic Venetian blind. The vertical "slats" of the filter physically block the horizontal waves of glare from passing through, while allowing useful, vertical ambient light to reach your eyes. This is how the lens surgically removes the visual noise without simply making everything dark.
Polarized vs. Non-Polarized Lenses: What's the Real Difference?
Understanding the distinction helps you choose the right tool for the job. While both reduce brightness, their method and results are fundamentally different. A non-polarized lens is a blunt instrument; a polarized lens is a surgical tool for enhancing vision.
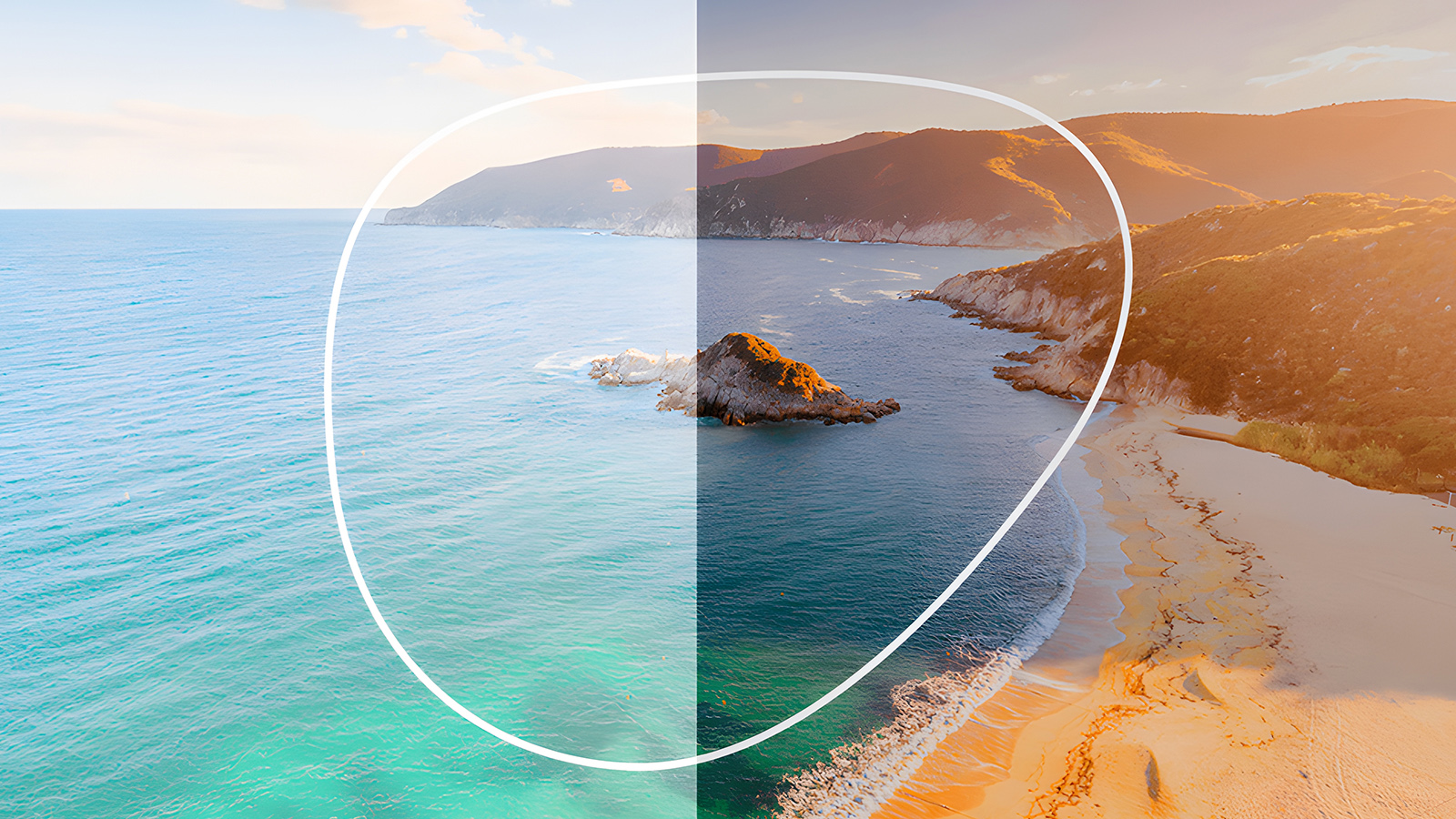

Here’s a direct comparison of how they stack up:
| Feature | Polarized Lenses | Non-Polarized Lenses |
| Primary Function | Selectively filters and eliminates horizontal glare. | Uniformly reduces the brightness of all light. |
| Glare Reduction | Excellent. Surgically removes distracting "visual noise." | Fair. Makes glare less bright but does not remove it. |
| Visual Clarity | High. Images appear sharper with enhanced contrast. | Standard. The entire scene is simply made darker. |
| Color Perception | Enhanced. Colors appear more vibrant, rich, and true. | Muted. A dark tint is applied uniformly over all colors. |
| Best For | Driving, fishing, water sports, and most high-glare environments. | General use, skiing/snowboarding, or when viewing LCD screens is critical. |
In short, a polarized lens actively improves the quality of visual information reaching your eyes by removing disruptive noise. A non-polarized lens simply turns down the volume on everything, including the details you want to see.
Are Polarized Sunglasses Actually Better for You?
For most bright, high-glare situations, the answer is a resounding yes. Adding a polarized option to your favorite Vooglam frames isn't just about looks; it’s about upgrading your visual experience for better comfort and safety.
- On the Road: Polarization drastically reduces glare from wet asphalt and other cars, helping you see road markings more clearly and preventing moments of temporary blindness. This significantly reduces driver fatigue on long trips.
- On the Water: This is where polarization is transformative. Eliminating the blinding glare from the water's surface provides a "see-through" advantage. Anglers can spot fish and underwater structures, while boaters can identify submerged hazards.
- General Outdoor Use: For activities like hiking or relaxing at the beach, polarization cuts through atmospheric haze, making scenery appear more vibrant and reducing the eye strain that leads to fatigue and headaches.
When Polarization Might Not Be the Best Choice
Despite their incredible benefits, polarized lenses aren't perfect for every single situation. Their unique filtering properties can be a drawback in specific scenarios.
Viewing Digital Screens
Because LCD and LED screens (like on your phone, GPS, or in a cockpit) emit polarized light, your sunglasses can interfere with them. This can cause the screen to look distorted, rainbow-colored, or completely black. For pilots and some equipment operators, this is a critical safety issue.
The 'Glare Paradox': Skiing and Icy Conditions
In some cases, glare is essential information. Skiers and snowboarders rely on seeing the sheen of glare to identify dangerous ice patches on the slopes. Polarized lenses can make these hazards invisible by eliminating that glare. For this reason, many winter athletes prefer non-polarized lenses for safety.
A Crucial Clarification: Polarization vs. UV Protection
This is the most important takeaway for your long-term eye health: polarization and UV protection are two completely separate and unrelated features.
- Polarization manages visible light to reduce harmful glare.
- UV Protection blocks invisible ultraviolet radiation (UVA and UVB) to prevent long-term eye damage.
The golden rule is that UV protection is the non-negotiable foundation of any quality pair of sunglasses. The American Academy of Ophthalmology stresses that you should always choose sunglasses that block 99% to 100% of UVA and UVB rays. At Vooglam, your eye health is our top priority. The vast majority of our lenses provide full UV400 protection, blocking 100% of harmful UVA/UVB rays. For a small selection of our unique styles, we offer lenses with UV380 protection, ensuring you always receive a high standard of safety.
Conclusion: Make a Confident Choice
Now, you can tell if your sunglasses are polarized in seconds and understand the sophisticated science behind them. Polarization is a high-performance feature engineered to filter out the visual noise of glare, delivering a clearer, more comfortable, and more vibrant view of the world.
This knowledge empowers you to choose the perfect lenses for your lifestyle. Whether you’re learning about choosing the right frames for your face shape or are ready to start customizing a bold new pair of Vooglam glasses, you can now confidently select the features that will let you express yourself while seeing the world in the best possible light.

Vooglam Blog
Vooglam blog shares professional knowledge about eyeglass frames, lenses, etc., and provides help when purchasing and using eyewear products. At the same time, Vooglam focuses on fashion glasses to interpret the trend of glasses for you.

How to Look Good With Glasses: Style Your Hair, Outfits, and Accessories
For a long time, glasses were seen as a medical necessity—something you "had" to wear. But the narrative has flipped. Today, glasses are one of the most powerful accessories in your wardrobe. They fra
February 10,2026
Office to Gala: 3 Styling Formulas for Your Day-to-Night Wardrobe
We know the drill. You have a concept pitch at a creative studio at 2:00 PM, a gallery walk-through at 6:00 PM, and a live gig at a basement venue that doesn't even kick off until midnight. You are no
January 29,2026
Experimental Eyewear: When Glasses Become Wearable Art
From Function to FormWalk into any gallery opening in Berlin, Tokyo, or New York and you'll notice something: the people who actually care about design aren't wearing Persol or Oliver Peoples anymore.
January 27,2026
The Best Streetwear Sunglasses & Glasses of 2026 (Vooglam's Editor's Picks)
Streetwear eyewear has reached a turning point. What started as logo-heavy collaborations and hype drops has evolved into something more interesting: frames that prioritize actual design innovation al
January 27,2026